Preface
Pneumonia is a serious lung infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It can be caused by bacteria, contagions, or fungi and leads to inflammation in the lungs, making breathing difficult. However, pneumonia can come life- hanging , especially for children, If left undressed. In this composition, we will bandy the causes, symptoms, forestallment, and treatment of pneumonia to help you stay informed and cover your health.
What’s Pneumonia?
Pneumonia is an infection that causes inflammation in the air sacs( alveoli) of the lungs. These air sacs may fill with fluid or pus, leading to symptoms similar as coughing, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Types of Pneumonia
1. Bacterial Pneumonia – Caused by bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and frequently occurs after a cold or flu.
2. Viral Pneumonia – Caused by contagions similar as the influenza contagion or COVID- 19.
3. Fungal Pneumonia – Caused by fungi set up in soil or raspberry feces, common in people with weak vulnerable systems.
4. Aspiration Pneumonia – Occurs when food, liquids, or heave enter the lungs, leading to infection.
Causes and threat Factors of Pneumonia
Common Causes
- Bacteria and Contagions – The most common causes of pneumonia.
- Fungi – set up in certain surroundings, affecting people with weak impunity.
- gobbled Substances – similar as chemicals, food, or heave.
Threat Factors
- Age – babies, youthful children, and people over 65 are at advanced threat.
- Weakened Immune System – Due to conditions like HIV, cancer, or organ transplants.
- habitual conditions – similar as asthma, diabetes, or heart complaint.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption – Damage lung function and increase infection threat.
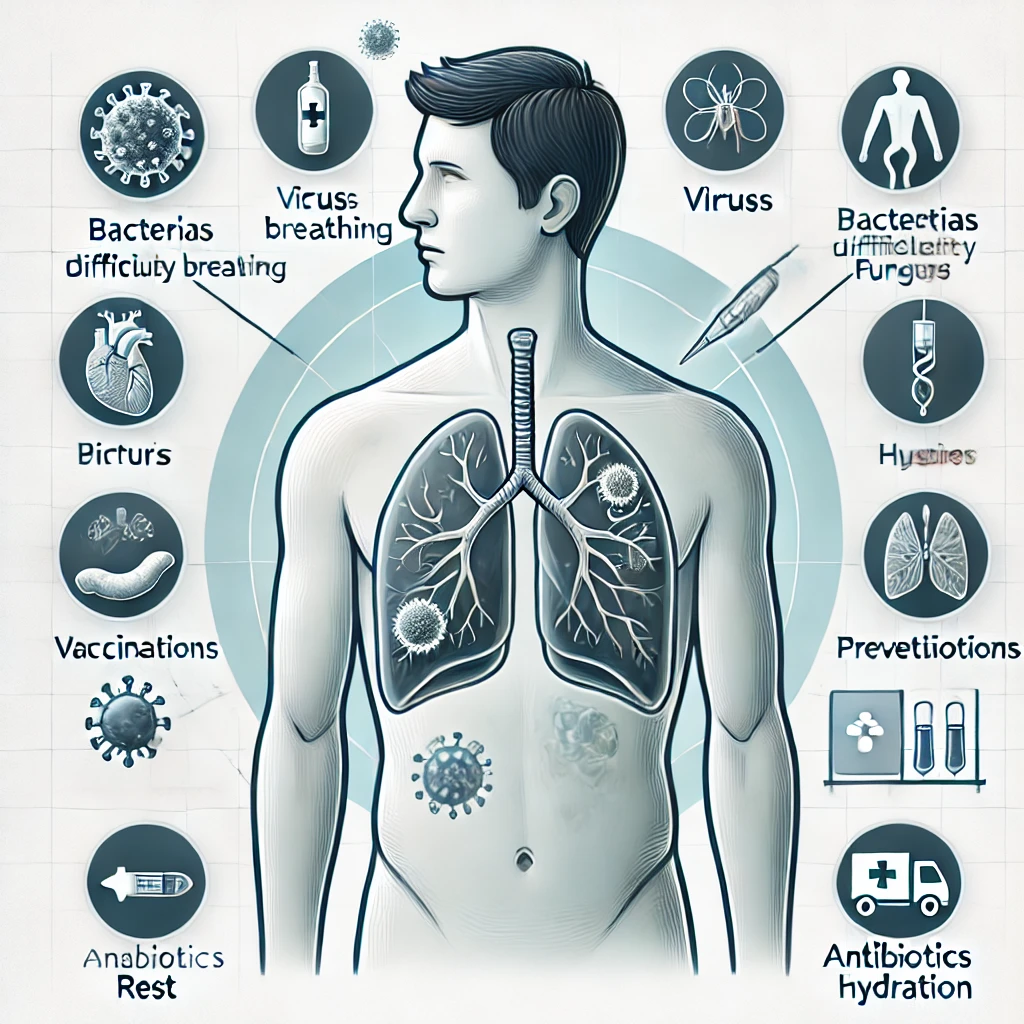
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Pneumonia symptoms can vary from mild to severe, depending on the cause and overall health of the case.
Common Symptoms
✅ Cough( with numbness or mucus)
✅ Fever and chills
✅ briefness of breath
✅ casket pain, especially when breathing or coughing
✅ Fatigue and weakness
✅ Loss of appetite
✅ Sweating and shaking chills Severe Symptoms( Seek Immediate Medical Help) , Bluish lips or fingertips( due to lack of oxygen), Confusion( especially in aged grown-ups), High fever( above 102 °F or 39 °C), Rapid or difficulty breathing .
How is Pneumonia Diagnosed?
Croakers diagnose pneumonia using the following styles Physical Examination – Checking for abnormal lung sounds. casket X-ray – Identifies lung infection and affected areas. Blood Tests – Detects infection and determines its cause. Sputum Test – Examines mucus for bacteria or contagions. palpitation Oximetry – Measures oxygen situations in the blood.
Prevention of Pneumonia
Taking preventative measures can significantly reduce the threat of developing pneumonia.
How to help Pneumonia
1. Get Vaccinated – Pneumococcal and flu vaccines help help bacterial and viral pneumonia.
2. Exercise Good Hygiene – Wash hands regularly to help infections.
3. Quit Smoking – Smoking weakens lung defenses, adding pneumonia threat.
4. Strengthen Your Immune System – Eat a balanced diet, exercise, and get enough sleep. 5. Avoid near communicate with Sick People – Reduces the threat of infection.
Treatment for Pneumonia
The treatment for pneumonia depends on its cause and inflexibility. Common Treatments Include
- Antibiotics – For bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral specifics – For viral pneumonia, similar as flu- related infections.
- Antifungal specifics – For fungal pneumonia.
- Rest and Hydration – Helps the body recover.
- Oxygen remedy – For severe cases with breathing difficulties. utmost mild cases can be treated at home, but severe cases may bear hospitalization.
For more detailed information on pneumonia symptoms, causes, and prevention, visit the official World Health Organization (WHO) website.